Clinical Manifestations
As IBD is a chronic intermittent disease, symptoms can range from mild to severe during relapses and may decrease or even disappear during remissions. Symptoms generally depend on the section of the bowel involved.
Ulcerative Colitis
UC consists of chronic intermittent periods of exacerbation and remission that occur unpredictably, but it can also appear as an acute crisis. The major symptoms are bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramping pain. In mild UC, less mucosa is involved so the frequency of bleeding, bowel movements and pain, is minimal. In moderate UC, there is an increase in stool output (4-5 per day), increased amount of bleeding, and increased systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, and anorexia. Severe forms of UC can involve the entire colon and are characterized by frequent bloody stools containing mucus (10-20 stools per day), urgency, tachycardia, and continuous and cramping pain. In addition, weight loss of more than 10% of total body weight, dehydration, fever, and anemia are present, resulting from fluid loss, bleeding, and inflammation.
Complications can include hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and perirectal abscess. Hemorrhage can result from inflamed, ulcerated mucosa, but severe hemorrhage is rare. The most common complications are fulminant colitis, bleeding, and toxic megacolon, which is extensive dilation and paralysis of the colon. Edema, fibrosis, and strictures can obstruct the colon. Perforation is possible although it is unusual, mostly occurring in the left side of the colon. Having UC for more than 10 years puts an individual at a greater risk of developing colorectal cancer. Extraintestinal manifestations include alterations in coagulation, hepatobiliary disease, and polyarthritis. The most common extraintestinal complications are skin lesions such as erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum.
Crohns Disease
Clinical manifestations of CD vary according to the anatomic site involved, the extent of the disease process, and the presence of complications. Onset of symptoms is usually insidious with nonspecific complaints. The major symptoms are diarrhea and abdominal pain, and occasionally, rectal bleeding if the colon is involved. The diarrhea is usually non-bloody and results from inflammation or malabsorption. The pain can be severe and intermittent, or constant. Weight loss, fatigue, and fever can accompany CD. Other manifestations include abdominal cramping, tenderness, and distension. Malabsorption of vitamin B12 (leading to anemia) and vitamin D can occur. Folic acid can be deficient and proteins may be lost (leading to hypoalbuminemia). Extraintestinal manifestations can include arthritis and finger clubbing. As the disease progresses, malnutrition, weight loss, electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, anemia, increased peristalsis, right lower quadrant and umbilical pain, and perianal disease can occur.
Complications include strictures and obstruction, fistulas between segments of the bowel, cutaneous fistulas, and urinary tract infections from fistulas that communicate with the urinary tract. Perforations, peritonitis, and formation of intra-abdominal abscesses can occur as a result of the inflammation of the bowels that may involve all layers. Damage to the intestinal mucosa causes the impaired absorption that leads to nutritional abnormalities. Extraintestinal complications are similar to those of UC and include renal disorders such as nephrolithiasis, ankylosing spondylitis, pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum, uveitis, liver disease cholelithiasis, and arthritis.
Clinical manifestations and complications of IBD are summarized in the following chart:
,
| Ulceraterive Colitis | Crohn's Disease |
| Clinical Manifestations | | |
| Diarrhea | Common; 4 times/ day | Common(May or may not be present)
|
| Blood stools | Common | Less common |
| Abdominal pain | Mild to severe | Moderate to severe
|
| Cramping | Possible | Common |
| Rectal Bleeding | Common | Fairly common |
| Abdominal mass | Rare | Common |
| Weight loss | Common | Common/Severe |
| Fever(intermittent) | During acute episodes | Common |
| Tenesmus | Severe | Rare |
| Malabsorption and Nutritional deficiences | None/Minimal incidence | Common |
| Co-Morbities | Extraintestinal manifestations | Extraintestinal manifestations |
| Clinical Course | Exacerbations and remissions | Exacerbations and remissions |
| Complications | | |
| Fistula | Rare | Common |
| Anal abcesses | Rare | Common |
| Strictures | Rare | Common |
| Perforation | Common | Common |
| Toxic megacolon | Common | Rare |
| Carcinoma | Increased incidence after 10 years | Slightly greater than the general population |
| Recurrence after surgery | Cure with Colectomy | 40 - 60% or more recurrence after segmental resection of the small or large bowel |
Previous Section: Pathogenesis
Home
Next Section:Treatment

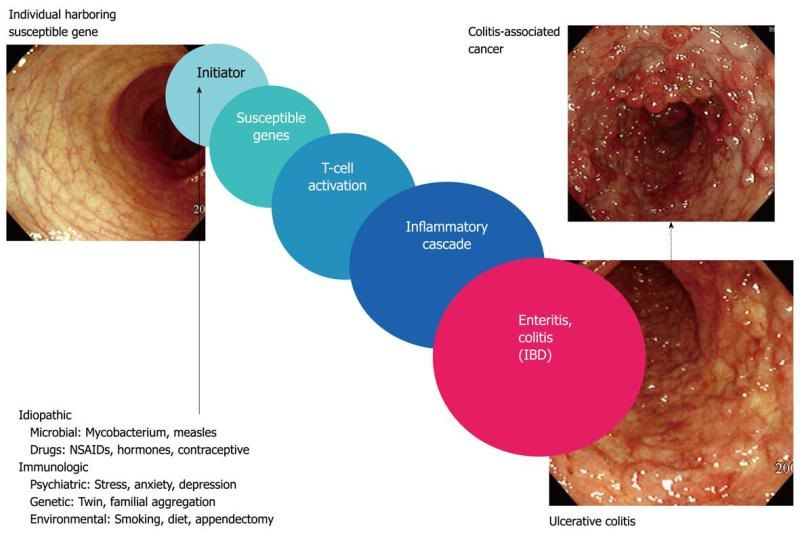
 Cigarette smoking plays an integral role in the development of CD. Although cigerette smoking does play an important role in the development of UC, it is important to note that people who frequently develop UC are non smokers.Smoking affects both systemic and mucosal immunity, altering a wide range , altering a wide range of both innate and adaptive immune functions. Smoking Alters the ratio of T-helper to T-Suppressor cells, reduces T cell proliferation, modulates apoptosis and significantly decreases serum and mucosal immunoglobulin levels. Furthermore, smoking enhances small bowel permeability and colonic mucus production.
Cigarette smoking plays an integral role in the development of CD. Although cigerette smoking does play an important role in the development of UC, it is important to note that people who frequently develop UC are non smokers.Smoking affects both systemic and mucosal immunity, altering a wide range , altering a wide range of both innate and adaptive immune functions. Smoking Alters the ratio of T-helper to T-Suppressor cells, reduces T cell proliferation, modulates apoptosis and significantly decreases serum and mucosal immunoglobulin levels. Furthermore, smoking enhances small bowel permeability and colonic mucus production.  Drugs such as oral contraceptives and NSAIDs have been hypothesized to correlates with the development of both UC and CD. Although proof that oral contraceptive, may cause IBD is ambiguous,studies have found that NSAIDs accelerate an in some cases worsen the colonic inflammation associated with blockade of protective prostaglandins and altered mucosal immune activity.
Drugs such as oral contraceptives and NSAIDs have been hypothesized to correlates with the development of both UC and CD. Although proof that oral contraceptive, may cause IBD is ambiguous,studies have found that NSAIDs accelerate an in some cases worsen the colonic inflammation associated with blockade of protective prostaglandins and altered mucosal immune activity.
 Although stress has not been identified as a primary cause of IDB in and of itself, it has been known to modulate the course of IDB. The exact mechanism underlying stress-induced exacerbation of IDB is unknown.
Although stress has not been identified as a primary cause of IDB in and of itself, it has been known to modulate the course of IDB. The exact mechanism underlying stress-induced exacerbation of IDB is unknown.
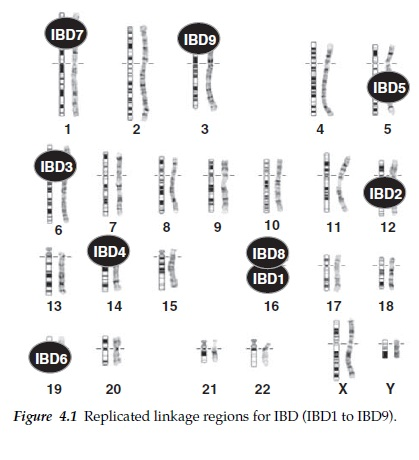
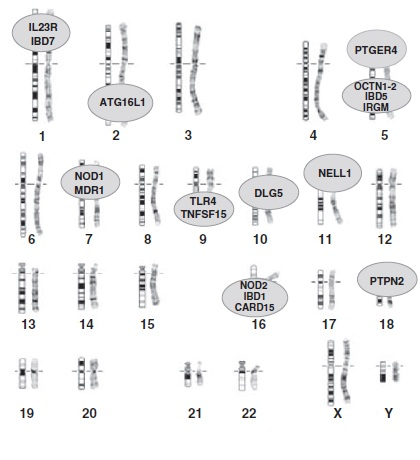
 It is characterized by inflammation of segments of the GI tract.
It is characterized by inflammation of segments of the GI tract.